Pruning hazelnut trees is essential for improving nut harvest efficiency. Proper pruning enhances tree structure, increases sunlight exposure, and promotes healthier growth. With the right techniques, growers can maximize yield and maintain tree vitality over time.
Hazelnut trees, known scientifically as Corylus avellana, are valued for their delicious nuts. These trees thrive in temperate climates and require specific care to flourish. Among the various maintenance practices, pruning stands out as a critical task that directly influences the quality and quantity of nut production. Regular pruning not only helps in shaping the tree but also plays a significant role in disease prevention and overall tree health.

Understanding the life cycle and growth patterns of hazelnut trees is important for effective pruning. Hazelnut trees typically begin producing nuts in three to five years and can remain productive for several decades with proper care. However, without appropriate pruning, trees may become overgrown and less productive. This can lead to reduced air circulation and light penetration, which are vital for healthy nut development.
The Importance of Pruning Hazelnut Trees
Pruning serves multiple purposes in hazelnut cultivation. It helps to:
- Enhance sunlight penetration into the canopy
- Improve air circulation among branches
- Facilitate easier harvesting
- Encourage new growth and nut production
- Reduce the risk of diseases and pests
Through these benefits, pruning contributes significantly to the efficiency of hazelnut harvesting. A well-pruned tree can yield more nuts of higher quality compared to a neglected one. Furthermore, proper spacing between branches allows for better access during harvest, reducing labor costs and time.

The timing of pruning is also crucial. It is generally recommended to prune hazelnut trees during late winter or early spring, just before the buds begin to swell. This timing minimizes stress on the tree and reduces the risk of frost damage to fresh cuts. Additionally, pruning at this time encourages vigorous growth in the growing season.
Common Pruning Techniques
There are several techniques that growers can employ when pruning hazelnut trees. Each method serves different purposes based on the age and condition of the tree:
1. Thinning
This technique involves removing specific branches to enhance light exposure and air circulation within the canopy. Thinning helps avoid overcrowding and ensures that resources are allocated efficiently among remaining branches.
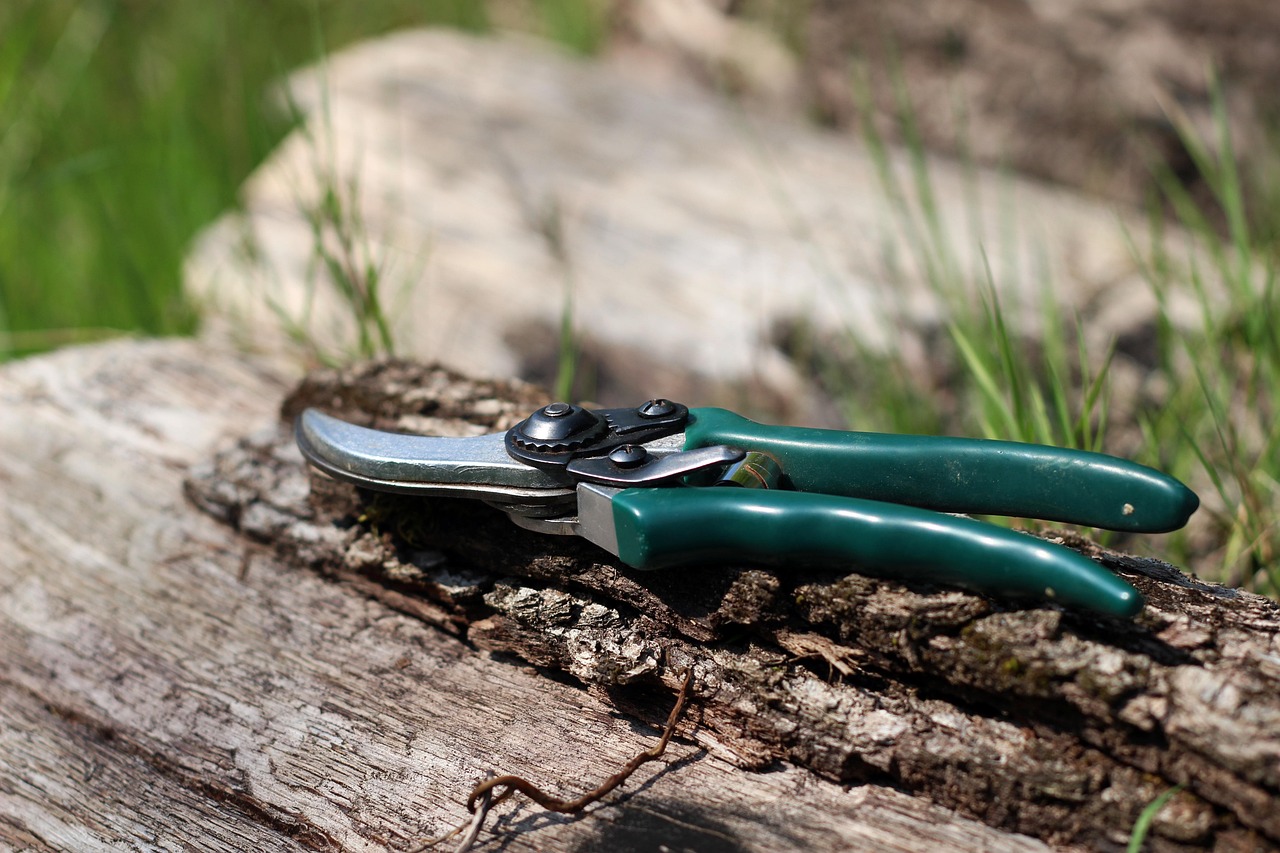

2. Heading Back
Heading back involves cutting the ends of branches to promote bushier growth. This technique is particularly useful for younger trees. By encouraging lateral branching, growers can create a fuller tree structure that supports more nuts.
3. Renewal Pruning
For older trees, renewal pruning is critical. This process includes cutting back older branches to encourage new growth from the base. It revitalizes the tree and can lead to increased nut production as younger branches typically produce more fruit.
Factors Influencing Pruning Decisions
Several factors can influence how and when to prune hazelnut trees:
- Tree Age: Younger trees may require more formative pruning, while older trees may need renewal techniques.
- Tree Health: Diseased or damaged branches should be removed promptly to prevent spreading.
- Variety: Different varieties of hazelnut may have unique growth habits that influence pruning practices.
- Climate: Local climate conditions can affect growth patterns and thus influence timing and techniques.
The interplay of these factors makes it essential for growers to assess their specific situations regularly. Tailoring pruning approaches based on individual needs ensures optimal tree health and productivity.
Tools Required for Pruning
Having the right tools is vital for effective pruning. The following tools are commonly used in hazelnut tree pruning:
- Hand Pruners: Ideal for small branches.
- Loppers: Useful for larger branches that require more leverage.
- Saws: Needed for thick branches that cannot be cut with pruners or loppers.
- Safety Gear: Gloves and goggles should always be worn to protect against cuts and debris.
Using sharp tools is crucial for making clean cuts. Clean cuts heal faster and reduce the likelihood of disease entering through wounds. Regular maintenance of tools ensures efficiency during pruning sessions.
In summary, understanding the significance of proper pruning techniques can greatly enhance the efficiency of nut harvesting in hazelnut trees. Growers who invest time in learning about these practices will likely see improved yields and healthier orchards over time.
Understanding Hazelnut Tree Growth Patterns
To effectively prune hazelnut trees, it is essential to understand their growth patterns. Hazelnut trees grow in a particular way that influences how they should be pruned. These trees typically exhibit a vigorous growth habit, producing both vertical shoots and lateral branches. Understanding these patterns helps growers make informed decisions about which branches to prune and when.
Hazelnut trees are deciduous and go through a cycle of growth and dormancy. During the growing season, they produce leaves, flowers, and ultimately nuts. The growth period generally starts in spring and can last until late summer. The following factors play a crucial role in the growth of hazelnut trees:
- Temperature: Hazelnut trees thrive in temperate climates with moderate temperatures.
- Soil Quality: Well-drained, nutrient-rich soil supports healthy growth.
- Water Availability: Adequate moisture is necessary during the growing season.
- Sunlight: Full sun exposure promotes better nut production.
Identifying the Best Pruning Time
The timing of pruning is vital for ensuring the health and productivity of hazelnut trees. Pruning at the right time can stimulate growth and improve nut quality. Growers should consider the following guidelines for optimal pruning times:
- Late Winter to Early Spring: This is the most recommended time for pruning as trees are still dormant. It minimizes stress and reduces the risk of frost damage.
- Post-Harvest Pruning: Some growers prefer to prune immediately after the nut harvest to prepare for the next growing season.
- Avoiding Late Pruning: Pruning too late in the spring can lead to excessive sap loss, which may weaken the tree.
By adhering to these timing guidelines, growers can maximize the effectiveness of their pruning efforts and enhance the overall health of their trees.
Pruning Hazelnut Trees: Step-by-Step Guide
A systematic approach to pruning hazelnut trees can yield better results. Here is a step-by-step guide that growers can follow:
- Assess the Tree: Before pruning, evaluate the overall health and structure of the tree. Look for dead or damaged branches as well as areas that are overcrowded.
- Remove Dead or Damaged Branches: Start by cutting away any dead, diseased, or broken branches. This helps prevent disease spread and allows the tree to focus energy on healthy growth.
- Thin Out Crowded Areas: Identify branches that cross each other or grow inward toward the center of the tree. Remove these branches to improve air circulation and light penetration.
- Shorten Long Branches: For long, leggy branches, use heading back techniques to encourage bushier growth. Cut back to just above a bud that faces outward.
- Maintain Shape: Ensure that the overall shape of the tree is balanced and open. This promotes better growth and easier harvesting.
This structured approach simplifies the pruning process and helps ensure that no critical steps are overlooked.
Common Mistakes in Pruning
Even experienced growers can make mistakes when pruning hazelnut trees. Being aware of some common pitfalls can help avoid them:
- Over-Pruning: Removing too much foliage can stress the tree and reduce nut yield. It is important to prune judiciously.
- Poor Timing: Pruning at the wrong time, such as during active growth, can harm the tree’s health and sap flow.
- Lack of Planning: Not having a clear pruning plan can lead to haphazard cuts that affect tree structure negatively.
- Ignoring Safety Precautions: Failing to wear appropriate safety gear can result in injuries during pruning activities.
Avoiding these mistakes can improve not only the health of the trees but also the efficiency of nut harvesting.
Pest and Disease Management During Pruning
Pest and disease management is an integral part of pruning hazelnut trees. Regular pruning helps remove infected branches and prevents diseases from spreading. Growers should be vigilant about common pests and diseases that may affect hazelnuts:
| Pest/Disease | Description | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Filbert Blight | A fungal disease that causes branch dieback. | Remove infected branches; apply fungicides if necessary. |
| Nutsedge | A weed that competes with hazelnuts for nutrients. | Implement proper weed management practices. |
| Spider Mites | Pests that feed on leaves, causing discoloration. | Use insecticidal soaps or predatory insects for control. |
| Corylus Aphids | Aphids that suck sap from new shoots. | Introduce beneficial insects or apply insecticides when necessary. |
By incorporating pest and disease management strategies into pruning practices, growers can maintain healthier orchards and improve nut yields for years to come.
Post-Pruning Care for Hazelnut Trees
After pruning hazelnut trees, proper care is essential to ensure that the trees recover quickly and continue to thrive. Post-pruning care involves several practices that support healthy regrowth and enhance overall tree vitality. This section outlines key strategies for effective post-pruning care.
Watering and Irrigation
Watering is one of the most critical aspects of post-pruning care. After pruning, trees may experience stress, making adequate moisture vital for recovery. The following guidelines can help ensure proper watering:
- Monitor Soil Moisture: Check the soil regularly to ensure it remains consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Avoid Overwatering: Excess water can lead to root rot. Ensure proper drainage in the planting area.
- Deep Watering: Water deeply to encourage roots to grow deeper into the soil, enhancing stability and nutrient access.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the tree to retain moisture and regulate soil temperature.
Nutrient Management
Providing adequate nutrients is crucial for the recovery process after pruning. Hazelnut trees require a balanced supply of macronutrients and micronutrients. Consider the following approaches:
- Soil Testing: Conduct soil tests to determine nutrient levels and deficiencies.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer based on soil test results. A nitrogen-rich fertilizer can promote new growth.
- Organic Amendments: Incorporate compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil structure and nutrient availability.
Nutrient management should be tailored to the specific needs of the trees, taking into account factors such as age, health, and soil conditions.
Monitoring Tree Health
After pruning, it is essential to monitor the health of hazelnut trees closely. Regular inspections can help identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention. Key aspects to monitor include:
- New Growth: Observe for healthy new shoots emerging from pruned areas. This indicates successful recovery.
- Pest Activity: Keep an eye out for signs of pests or diseases that may threaten tree health.
- Leaf Color and Texture: Healthy leaves should be bright green and free from spots or discoloration.
- Fruit Development: Monitor the formation of nuts during the growing season to gauge overall tree productivity.
Seasonal Pruning Considerations
Pruning practices may vary depending on the season, and understanding seasonal considerations can enhance pruning effectiveness. Here are some seasonal tips for maintaining hazelnut trees:
Spring Pruning
Spring is an active growth period for hazelnut trees. Pruning during this time can stimulate new growth. However, care should be taken not to prune too late in the season when sap flow increases. Focus on:
- Removing any winter-damaged branches.
- Thinning crowded areas to allow light penetration.
Summer Pruning
Summer pruning can help manage growth and shape the tree. This practice is typically less intensive than spring pruning and involves:
- Removing unwanted suckers or water sprouts that can detract from nut production.
- Making minor adjustments to maintain tree shape without stressing the tree.
Fall Pruning
Fall is generally not recommended for heavy pruning due to the risk of exposing trees to winter damage. However, light maintenance can be done by:
- Clearing away fallen debris to minimize disease risk.
- Assessing tree structure for any necessary adjustments before winter dormancy.
The Role of Mulching in Tree Health
Mulching plays a significant role in maintaining tree health after pruning. It provides numerous benefits that support growth and development:
- Moisture Retention: Mulch helps retain soil moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering.
- Weed Suppression: A layer of mulch can inhibit weed growth, reducing competition for nutrients and water.
- Soil Temperature Regulation: Mulch acts as an insulator, keeping soil temperatures stable during extreme weather conditions.
- Nutrient Supply: Organic mulches decompose over time, adding valuable nutrients back into the soil.
Selecting the right type of mulch is essential. Organic materials such as wood chips, straw, or shredded leaves are often preferred due to their additional benefits for soil health.
Pest and Disease Prevention Strategies
Preventing pests and diseases is crucial in maintaining the health of hazelnut trees after pruning. Implementing proactive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of infestations:
- Cultural Practices: Maintain proper spacing between trees to improve air circulation and reduce humidity around foliage.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic checks for early signs of pests or diseases. Early detection allows for prompt action.
- Sanitation Measures: Remove fallen leaves and debris that can harbor pests or pathogens.
- Diverse Planting: Consider planting companion plants that attract beneficial insects and deter harmful pests.
By incorporating these strategies into regular maintenance routines, growers can create a healthier environment for hazelnut trees, ultimately leading to improved nut yields and overall orchard vitality.
Maximizing Nut Quality Through Pruning Techniques
In addition to enhancing harvest efficiency, effective pruning techniques can significantly influence the quality of the nuts produced by hazelnut trees. Quality nuts are larger, healthier, and more flavorful, which can lead to better market prices and consumer satisfaction. Here are some strategies to ensure high-quality nut production through proper pruning:
- Focus on Fruit-Bearing Wood: Prioritize pruning techniques that enhance the development of fruit-bearing wood. This includes encouraging lateral branches that are known to produce higher quality nuts.
- Maintain Tree Height: Keeping trees at a manageable height not only facilitates easier harvesting but also ensures that all parts of the tree receive adequate sunlight and air circulation.
- Remove Non-Productive Branches: Regularly evaluate and remove branches that do not produce nuts or have poor nut quality. This allows the tree to redirect energy toward more productive areas.
- Encourage Balanced Growth: Evenly distribute growth among branches to prevent overcrowding and ensure that each branch can yield quality nuts.
By focusing on these techniques during the pruning process, growers can improve nut quality, leading to increased profitability and customer satisfaction.
Long-Term Orchard Management Practices
Effective hazelnut tree pruning is just one aspect of long-term orchard management. To maintain a productive and healthy orchard over the years, growers should consider the following long-term practices:
- Regular Soil Testing: Conduct soil tests every few years to monitor nutrient levels and pH. Adjust fertilization based on these findings to maintain optimal soil health.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Implement an IPM approach by combining biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical control methods. This holistic strategy helps manage pests while minimizing environmental impact.
- Crop Rotation and Diversification: Consider planting cover crops or diversifying crops in the orchard to enhance soil fertility and disrupt pest cycles.
- Continuous Education: Stay informed about new research, pest management strategies, and best practices in hazelnut cultivation by participating in workshops, seminars, and agricultural extension programs.
These long-term management practices will substantially contribute to the sustainability and productivity of hazelnut orchards, ensuring that they remain viable for years to come.
The Economic Impact of Efficient Pruning
The economic benefits of efficient pruning practices extend beyond immediate yield improvements. By maximizing nut harvest efficiency through proper pruning techniques, growers can achieve significant cost savings and revenue increases over time. Here are some economic impacts to consider:
- Reduced Labor Costs: Efficiently pruned trees are easier to harvest, reducing labor time and associated costs during the nut harvesting season.
- Higher Yields: Improved nut production directly correlates with increased revenue per acre, allowing growers to maximize their profits.
- Enhanced Market Value: Higher quality nuts often fetch better prices in the market, leading to increased profitability for growers who prioritize quality through effective pruning.
- Longer Tree Lifespan: Proper pruning contributes to the overall health of trees, potentially extending their productive lifespan and allowing for continued harvests over many years.
By recognizing and leveraging these economic impacts, hazelnut growers can make informed decisions that benefit both their operations and their bottom line.
Conclusion
Pruning hazelnut trees is a critical practice that significantly affects nut harvest efficiency, quality, and overall orchard health. Through understanding tree growth patterns, implementing effective pruning techniques, and maintaining diligent post-pruning care, growers can enhance their productivity and profitability. Additionally, integrating long-term management practices and monitoring tree health will contribute to sustainable orchard operations.
The combination of these strategies creates a solid foundation for a successful hazelnut farming venture. As the demand for high-quality hazelnuts continues to rise, growers who invest time and resources into mastering pruning techniques will likely see enhanced yields and improved market competitiveness. Ultimately, effective hazelnut tree pruning is not just about cutting branches; it’s about cultivating a thriving ecosystem that supports healthy trees and bountiful harvests for years to come.
